The following article describes the challenges parents, teachers, and students have when facing deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and difficulty with attention. We will explore the issues, impacts and solutions associated with supporting students with ADHD, including the top ADHD classroom tools you can use if your child or teen has this condition.
Jane had always noticed her son Liam’s boundless energy and his tendency to lack concentration, constantly fidget, make careless mistakes, and not make eye contact. At first, she simply thought Liam was a vivacious little boy who loved to talk and talk and talk.
However, during second grade, his teacher suggested they might be signs of something more. After consultations and evaluations, the diagnosis was clear: Liam had attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
It was a relief to finally have a name for what Jane, her spouse and Liam were experiencing, but it also brought many questions: how could they support Liam’s learning at school and home? It seemed like such a daunting task.
The answer revealed itself when Liam’s school introduced specialized ADHD classroom tools, thanks to the help of special education services. Noise-canceling headphones to help him focus, a discreet pedal device under his desk for his restless legs, and a variety of fidget tools and sensory strips as outlets for his excess energy and impulsive behavior.
Fidget tools also contributed to enhancing his fine motor skills and completing complex tasks. These ADHD tools for students, simple yet effective, provided Liam with the support he needed to match his intelligence with his academic potential, offering a tangible sense of progress and easing his parents’ concerns.
Educators and students alike deal with distinct complications when ADHD is part of the learning equation. It’s not just about maintaining attention in children or managing impulsivity; it’s about understanding and drawing out the potential of every student. ADHD tools for the classroom are essential solutions for children’s learning. They are serving as bridges over the hurdles that ADHD can present.
We’ve curated a wide range of information on these ADHD tools for students. We are offering insights for parents and teachers to foster a thriving educational experience.
ADHD Classroom Tools and Strategies for Enhancing Concentration
Despite the challenges that students with ADHD endure, there is considerable hope and many paths to academic success. Innovations in educational strategies and ADHD tools for the classroom have opened new doors, offering effective ways to improve students’ concentration and learning.
These ADHD tools for students are specifically designed to align with the unique needs of students with ADHD, transforming potential obstacles into opportunities for growth and engagement. By leveraging these resources, students can experience a significant improvement in their ability to focus and thrive academically.
Fidget Tools
Fidgeting, a common characteristic among students with ADHD, doesn’t have to be a barrier to learning. In fact, when channelled correctly, it can become a means for improving focus.
Understanding this, educators and experts have developed various fidget tools that help students utilize their natural energy and restlessness in a positive and productive manner.
These fidget tools, integrated into the classroom setting, can provide discreet yet effective ways for students to manage their need for movement and sensory input while focusing on their learning tasks. They can also help to develop their motor skills.
We have selected some of the best fidget tools for students with ADHD. Many of the ADHD fidget tools listed below can be found on Amazon for very affordable prices.

Fidget labels and sensory strips:
Small, tactile stickers that can be attached to a desk or notebook. By engaging in tracing and breathing exercises with fidget devices, students can improve concentration and reduce restlessness. Fidget labels can be stuck on a wall, a desk, or an item in a quiet corner of the classroom.

Soft, pliable balls, also known as stress balls, that can be squeezed to improve focus. You can learn more about the benefits of squeeze balls for children here.

Swivel chairs, wobble chairs and disk seats
Alternative seating options to support kids’ need for sensory stimulation.
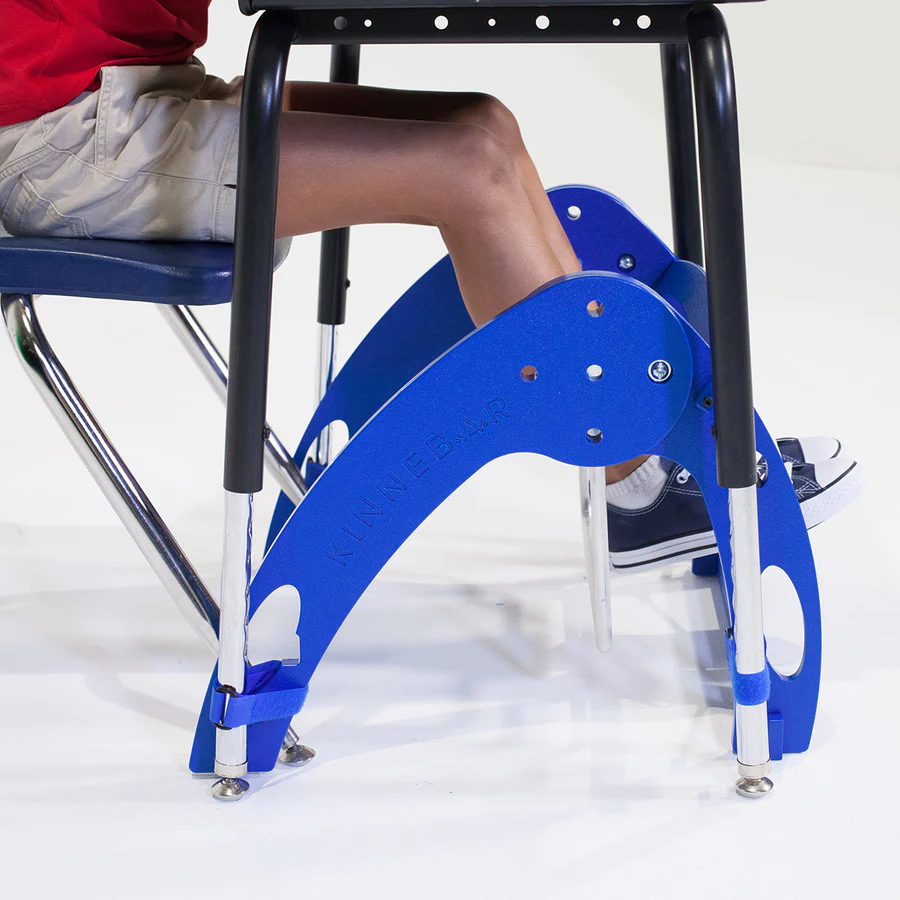

Swinging footrests under a desk
Desks equipped with a footrest for movement.
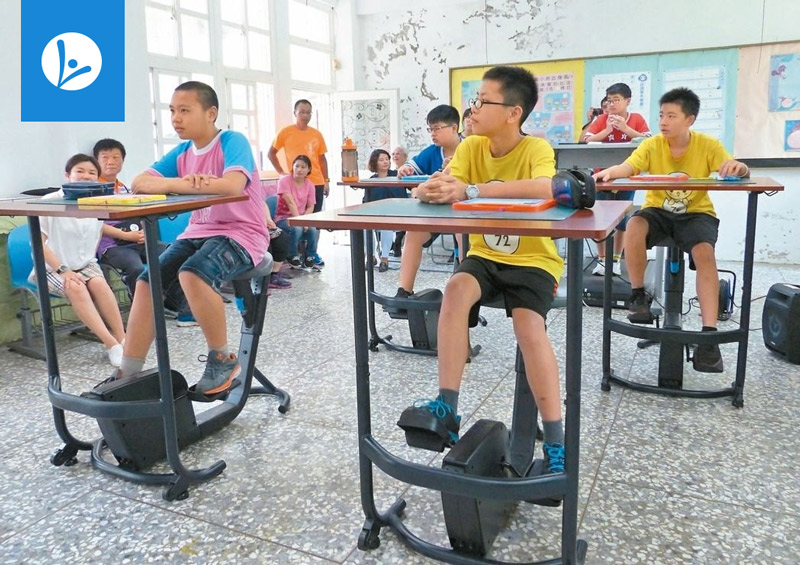

Stationary bikes or other kinetic desks
Small bikes, for example, are placed under desks for pedalling.
Assistive Learning and ADHD Tools for Students
In today’s digital age, a variety of innovative tools and technologies are available to support ADHD students in their education and daily routines, regardless of their ages.
These assistive learning tools, often in the form of fun video games, are designed to cater to the individual learning requirements and stumbling blocks encountered by students with ADHD, helping them to stay engaged, organized, and motivated. They play an important role in individualized education programs. Let’s explore these ADHD tools for students in more detail.
Reading Tools

Reading can be very difficult for students with ADHD, as it requires sustained focus and comprehension. Many reading tools have been developed to make reading more interactive and engaging, improving focus and comprehension through features like text-to-speech and interactive digital books.
Here are some options:
- Text-to-Speech: Software like Learning Ally Audio, and Voice Dream Reader.
- Apple Books and Audible: Digital books with interactive features.
- Rhyme to Read: An app that helps with reading through rhyming.
Math Assistance
Mathematics often involves abstract concepts that can be difficult for ADHD students to grasp. Math assistance tools are designed to make learning these concepts more tangible and enjoyable. By integrating movement and gaming elements, these ADHD tools for the classroom help kids understand and retain math concepts in a fun and interactive way.
Explore these:
- Math vs Zombies: Games that teach math all while having fun fighting off zombie invasions.
- Sushi Monster: A collaborative math game involving sushi plates.
- Motion Math Zoom: A game that combines math problems with fun gameplay with animals.
Writing Aids
Writing requires organization of thoughts and ideas, which can be daunting for students with ADHD. Additionally, writing aids are instrumental in helping these students structure their thoughts and enhance their writing skills. These tools offer visual organization, creative story-building, and spelling assistance, making writing a more manageable and enjoyable process.
Check out:
- MindNode: An app for organizing thoughts and ideas visually.
- Storybird: A tool for creating visual storybooks.
- SpellBetter: An assistive writing app with spell check.
Organizational Tools
A lack of organization and a notion of time are common for students with ADHD. Organizational tools are designed to help these students more easily keep track of their tasks, assignments, and schedules. Such tools simplify the process of staying organized, reducing stress and enhancing productivity.
Explore these solutions:
- Anydo: An app for task management and organization.
- Todoist: A list-making tool for tracking assignments and tasks.
Gadgets for Learning
In a world where technology is constantly evolving, gadgets for learning have become an invaluable resource for students with ADHD. These gadgets, such as pens that record spoken words and scanning pens that read text aloud, provide tactile and auditory learning experiences. They help bridge the gap between traditional learning methods and the distinct needs of ADHD students.
Here are some ideas:
- LiveScribe: A pen that records spoken words and syncs them with written notes.
- WizCom Tech Pen: A scanning pen that reads text aloud.
Time Management Solutions
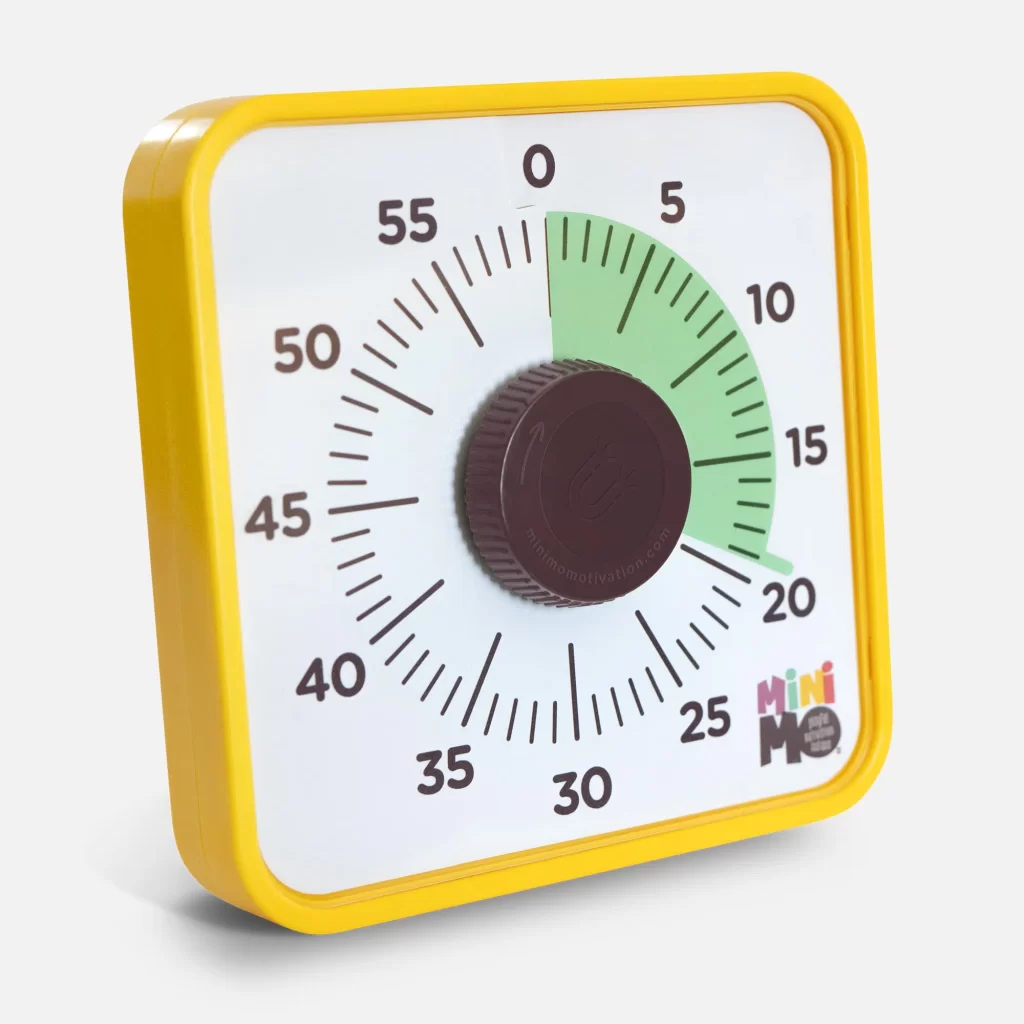
For students with ADHD, managing time effectively can be a significant hurdle. Time management solutions, such as visual timers, are specifically designed to help these students understand and track the passage of time. These tools aid in improving time awareness by providing a clear visual representation of time.
- Magnetic visual Timer: A visual timer that shows the passage of time.
How to Modify Learning Environments with ADHD Tools for the Classroom
Apart from these ADHD classroom tools, adjusting the classroom environment and teaching methods can play a crucial role in supporting students with ADHD. Special education services personnel can assist educators in better handling children with attention deficit disorders in the entire classroom.
Creating an inclusive classroom for children with ADHD involves a multifaceted approach based on diverse learning styles and needs. Teachers can start by structuring the classroom environment to reduce distractions and provide simple instructions
It’s also beneficial to allow for movement breaks, provide sensory tools, like fidget devices for concentration, and find ways for kids to learn fun time management. Assigning classroom responsibilities can foster a sense of belonging and self-worth.
Positive reinforcement and tailored support strategies, like breaking tasks into smaller steps, will help students with ADHD stay focused and organized.
By allowing students to draw or doodle quietly, teachers can provide an outlet for creative expression and cognitive processing. This activity engages different parts of the brain, which can aid in concentration and information retention. Additionally, doodling can be a subtle yet effective way to reduce stress and anxiety, making it easier for students to engage with the material being taught.
The integration of white noise or music in a classroom setting can have a profound impact on the learning environment. Calm sounds or carefully selected music can create a soothing backdrop that enhances students’ ability to stay focused. This auditory stimulation is particularly beneficial for students who may be easily distracted by the typical sounds of an entire class.
Rethinking the classroom’s physical layout can significantly improve students’ learning experience. Creating designated areas where students can stand or walk around allows them to manage their energy and stay engaged in learning.
Also, providing flexible work locations within the classroom empowers students to choose where they feel most comfortable and productive. This could include options like sitting at different desks, working at a standing desk, or even moving to a quiet corner.
Strategies for Managing ADHD Symptoms
To effectively manage ADHD symptoms in the classroom, teachers can adopt specific, actionable strategies. Eliminating distractions might involve seating students with ADHD away from windows, doors, or high-traffic areas of the classroom.
To prevent chattering and interruptions, teachers could introduce a ‘talking token’ system where only the student with the token may speak, thereby encouraging turn-taking and attentive listening.
Educators can use structured activities with clear, concise instructions and immediate consequences for rule-breaking to reduce impulsivity.
Calming fidgeting can be addressed by providing sensory toys or fidget tools, as listed above, that allow discreet movement without disrupting others. Furthermore, teaching and reinforcing following directions can be achieved through the use of visual cues, step-by-step checklists, and positive reinforcement techniques.
By applying these concrete methods, teachers can create an environment that not only manages ADHD symptoms but also significantly improves learning outcomes for these students.
Collaboration with School Staff
Practical support for ADHD students often requires collaboration with the entire school staff and parents. This includes regular team meetings with parents, teachers, counsellors, and special education professionals to develop a unified management plan tailored to each student’s needs.
Sharing specific strategies, such as using visual aids for those who struggle with verbal instructions or implementing a signal system to address behavioural issues discretely, can be beneficial. Setting up a structured routine that all teachers follow reduces unpredictability, which often triggers ADHD symptoms.
Moreover, establishing clear, measurable goals for academic and behavioural progress helps monitor the student’s development and make necessary adjustments.
It’s also vital to have open communication channels between staff and parents to ensure strategies are the same at school and home. Including regular, structured breaks for movement can help students with ADHD expend their energy and increase focus.
For school staff that are unfamiliar with ADHD, training is key. Armed with a better understanding of ADHD, teachers can educate and promote empathy among all students to encourage inclusivity.
Also, peer support programs can be established, enabling students to help one another and build a community of support, further normalizing ADHD and equipping students with the ability to advocate for and assist each other.
Ensuring Success for ADHD Students
Forming a supportive framework for students with ADHD, setting up classroom accommodations, and dedicating extra time to them are key to their success at school. This involves not only internal strategies within the classroom but also recognizing when parents should look for external support.
Seeking External Help for Students with ADHD
There comes a point in the educational path of a student with ADHD when school-based interventions are not enough. Acknowledging this need is the first step towards finding adequate resources outside the traditional classroom setting.
Exploring specialized brain training programs for kids and teenagers with ADHD, such as Brain Balance, which offer structured, comprehensive interventions for learning, can provide the extra layer of support that these students require to excel academically and socially.
A lot of current research and ensuing systematic reviews also advocate for getting kids with ADHD more active to ensure better cognitive control performance. A study conducted by T.A. Hartanto, Krafft CE, A.M. Iosif, and Schweitzer JBshowed that intense physical activity has the potential to boost cognitive performance.
Future studies are planned to explore how physical activity can be directly tied to students carrying out academic tasks and ensure emotional control.
In conclusion, the right strategies and tools can make a significant difference in the educational experiences of students with ADHD and the teaching strategies employed by educators.
By incorporating a variety of sensory tools for students, behavioral interventions, and effective strategies into the classroom, we can create an environment where all students have the opportunity to achieve their full potential each and every school day.
It’s all about understanding and tapping into each student’s strengths, providing them with the support they need, and celebrating every step of progress along the way.
Understanding ADHD and Its Impact on Learning
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, commonly known as ADHD, stands as the predominant psychiatric condition affecting children globally. Systematic reviews in research indicate that ADHD is a prevalent neurodevelopmental disorder that can significantly hinder a student’s capacity to learn, develop social skills, and engage in academic environments.
Unfortunately, some schools across North America don’t offer the right accommodations for students; they are only just beginning to modify their approaches to understand and support students with ADHD.
According to the Centre for ADHD Awareness Canada, ADHD is one of the most common neurodevelopment disorders in Canada, affecting 5-7% of children and 4-6% of adults. In the United States, the number of children between the ages of 3-17 that have been diagnosed with ADHD is 6 million, or 9.8%), as per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
What Is ADHD?
What exactly is ADHD? Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurological condition characterized by a pattern of short attention spans, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that is more pronounced than typical children’s developmental behaviours. In other words, ADHD is a different wiring of a child’s brain that affects their attention, activity levels, and impulse control.
Here is a list of the typical characteristics often seen in kids with ADHD. From elementary school to high school to college students:
- Inattentiveness: Difficulty in sustaining focus on tasks or activities, often seeming like they’re not listening when spoken to directly.
- Hyperactivity: Showing high levels of physical activity, restlessness or difficulty in staying seated in situations where it is expected.
- Impulsivity: Acting without thinking about the consequences, having difficulty waiting for their turn, and frequently interrupting conversations or activities.
- Disorganization: Struggling with organizing tasks and activities and leading to problems in managing time. It’s also meeting deadlines, and keeping track of personal items.
- Forgetfulness: Regularly forgetting to do chores, homework, or losing things necessary for tasks or activities.
- Frequent mood swings: Experiencing rapid, intense mood changes, and negative behavior, often in response to their surrounding environment
- Difficulty following instructions: Struggling to follow through on instructions and failing to finish schoolwork, chores, or duties in the workplace.
- Emotional sensitivity: Being easily frustrated, overwhelmed, or upset, often leading to emotional outbursts.
- Variable performance: Inconsistent performance in schoolwork, with a mix of high and low grades, often unrelated to intelligence or potential.
- Trouble socializing: Having difficulty in maintaining friendships and social relationships, often due to impulsivity or inattention during social situations.
Keep in mind that ADHD is different from another disorder called sensory processing disorder.
While ADHD is primarily related to attention and behavior regulation, SPD is more about how sensory information is perceived and processed in a person’s brain. It’s important to note that these disorders affect the behavior of students in different ways. They also require diverse types of management and intervention strategies.
The Challenges Students with ADHD Face in the Classroom
Often misconceived as merely a condition affecting overly active, undisciplined children who struggle to remain seated or lack motivation and self-control, ADHD is a more complex disorder. While it does involve obstacles in regulating attention, along with potential hyperactivity and impulsivity, extensive research shows its effects on students are far-reaching.
In fact, students with ADHD often navigate a maze of distractions that can make the traditional learning environment and academic performance feel like an uphill battle.
ADHD affects cognitive processing speed and executive functioning skills, which can impact the development of crucial academic abilities, such as reading fluency and comprehension, written expression, and mathematical problem-solving.
It also hampers acquiring vital learning, studying, and organizational strategies. ADHD is often associated with poor reading and math scores and overall lower grades.
What’s more, students with ADHD are often up against a distressing stigma, both from their peers and sometimes, unfortunately, from teaching staff. In the social microcosm of a classroom, these students can be unfairly labelled as disruptive or inattentive, leading to a sense of isolation and anxiety for the kid that has ADHAD—and widespread misunderstanding among their classmates.
These labels not only impact their social interactions but can also affect their self-esteem and academic motivation.
Some teachers, operating under time constraints and with limited resources, may become impatient towards the needs of students with ADHD. This impatience, often stemming from a lack of skills to support ADHD-related issues, can inadvertently reinforce negative stereotypes. It can also create an environment where these students struggle to learn.
It’s vital to foster a more empathetic and informed understanding of ADHD, promoting inclusive and supportive educational settings for all students.
As a result, students with ADHD are at a threefold higher risk of dropping out of high school compared to their peers.
Children and Adults with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (CHADD), an organization that empowers people affected by ADHD, points to several studies, including one by Kuriyan et al. (2013), that reveal significant educational disparities among young adults diagnosed with ADHD compared to their non-ADHD counterparts.
The study highlighted that students with ADHD were considerably less likely to pursue higher education. Specifically noting a reduced likelihood of enrolling in a four-year college. The disparity was stark, as these individual students were 11 times more likely to forego any form of higher education. This include vocational or junior colleges.
Furthermore, the attainment of advanced degrees was significantly lower among the ADHD group, with only 15% holding a four-year degree (versus 48% of the control group) and a mere 0.06% achieving a graduate degree, in contrast to 5.4% in the non-ADHD group.
This research underscores the educational problems met by individuals with ADHD, highlighting the need for tailored support and interventions at the onset of a child’s educational journey.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is assistive technology for ADHD students?
Assistive technology for ADHD students includes devices, software, or equipment that helps to compensate for their learning challenges during their school day
This can range from simple tools like noise-canceling headphones, fidget aids, and organizational skills and time management software. Examples include graphic organizers, electronic planners, text-to-speech and speech-to-text programs, and apps that block distracting websites.
How do students with ADHD learn best?
Students with ADHD often learn best through visual, auditory, and kinesthetic (hands-on) experiences. Structured and engaging lessons with clear, concise instructions can be helpful. They benefit from consistent routines, short learning sessions, interactive activities, and immediate feedback. Personalized learning strategies catering to individual needs and strengths also enhance learning outcomes.
What helps ADHD students focus?
Creating a distraction-free environment can help individual students with ADHD focus. This may include a quiet space, a clutter-free work area, and the use of timers. This will encourage short, focused work periods followed by breaks. ADHD tools for students, like fidget tools and fidget toys, can help some kids manage excess energy and maintain focus. Consistent routines and clear expectations are also important.
What are some ADHD tools for students?
ADHD tools for students include organizational apps, timers, and reminder systems to help with time management. There are also focus apps that limit access to distracting content on devices. Educational software that adapts to a student’s pace, note-taking applications, and mind-mapping tools can assist with learning.
For some, fidget tools and ergonomic chairs that allow movement can also be great options.